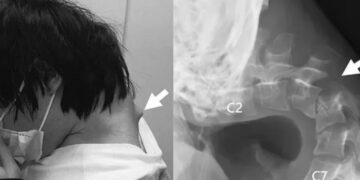
Imagine um mundo onde seu roteador Wi-Fi não apenas fornece internet, mas também atua como uma espécie de “câmera invisível”, capaz de detectar movimentos humanos através das paredes. Parece algo saído de um filme de ficção científica, certo? No entanto, essa realidade já está sendo desenvolvida por cientistas que estão transformando redes Wi-Fi em ferramentas avançadas de monitoramento humano.
Pesquisadores da Universidade Carnegie Mellon, nos Estados Unidos, estão na vanguarda dessa inovação. Eles criaram uma tecnologia que utiliza inteligência artificial (IA) e sinais de Wi-Fi para mapear corpos humanos e rastrear seus movimentos, tudo sem a necessidade de câmeras tradicionais ou sensores visuais. O sistema funciona analisando os sinais de rádio emitidos pelos roteadores Wi-Fi e interpretando como esses sinais se comportam ao interagir com objetos e pessoas no ambiente.
Como Funciona Essa Tecnologia?
Os pesquisadores usaram uma técnica chamada DensePose , desenvolvida inicialmente pelo Facebook (hoje Meta), para processar os dados dos sinais de Wi-Fi. Com isso, conseguiram criar representações digitais 2D de pessoas presentes no ambiente — algo semelhante a um mapa corporal virtual. Embora o modelo ainda esteja limitado a imagens bidimensionais, a equipe já planeja expandir sua capacidade para gerar modelos 3D no futuro.
O mais impressionante é que tudo isso acontece sem invadir a privacidade das pessoas. Diferente das câmeras, que capturam imagens claras de rostos e detalhes, o sistema baseado em Wi-Fi cria apenas formas abstratas, preservando a identidade dos indivíduos.
Por Que Isso É Importante?
1. Monitoramento de Idosos:
Imagine poder garantir a segurança de idosos sem a necessidade de câmeras intrusivas. O sistema pode detectar quedas, movimentos suspeitos ou até mesmo verificar se uma pessoa está seguindo sua rotina diária normal.
2. Segurança Residencial:
Esqueça alarmes convencionais. Com essa tecnologia, é possível detectar movimentos não autorizados dentro de casa, mesmo que o intruso esteja em um cômodo diferente.
3. Automação Residencial:
4. Saúde e Bem-Estar:
Mas Quais São os Desafios?
• Interferências e Obstáculos:
Sinais de Wi-Fi podem ser facilmente bloqueados por paredes grossas ou interferidos por outros dispositivos eletrônicos. Isso torna o sistema menos confiável em ambientes complexos.
• Privacidade e Regulamentação:
Apesar de ser considerada “privada”, a coleta de dados sobre movimentos humanos levanta questões éticas. Regulamentações como o GDPR (na Europa) exigem transparência e consentimento explícito para qualquer tipo de monitoramento, mesmo que não envolva imagens.
• Custo e Infraestrutura:
Muitos roteadores Wi-Fi disponíveis no mercado hoje não são projetados para fornecer os dados detalhados necessários para esse tipo de análise. Atualizar a infraestrutura pode ser caro, especialmente para grandes espaços comerciais ou públicos.
O Futuro Está Chegando
E enquanto outras tecnologias, como radar mmWave e LiDAR, oferecem alternativas para detecção humana, elas são muito mais caras e consomem mais energia. O uso de Wi-Fi, por outro lado, é escalável e aproveita a infraestrutura já existente em milhões de lares e escritórios.
Uma Nova Era de Monitoramento Invisível
Se você achou essa notícia curiosa e bizarra, prepare-se: o futuro está prestes a ficar ainda mais estranho — e fascinante.
Imagine a world where your Wi-Fi router does more than just provide internet—it also acts as a kind of “invisible camera,” capable of detecting human movements through walls. Sounds like something out of a science fiction movie, right? However, this reality is already being developed by scientists who are transforming Wi-Fi networks into advanced tools for human monitoring.
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University in the United States are at the forefront of this innovation. They have created a technology that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and Wi-Fi signals to map human bodies and track their movements without the need for traditional cameras or visual sensors. The system works by analyzing radio signals emitted by Wi-Fi routers and interpreting how these signals behave when interacting with objects and people in the environment.
How Does This Technology Work?
The magic behind this invention lies in the concept of Channel State Information (CSI) . When Wi-Fi signals travel through the air, they reflect, bend, or scatter when encountering obstacles like walls, furniture, or human bodies. These subtle changes in the signals can be captured and analyzed by AI algorithms.
The researchers used a technique called DensePose , initially developed by Facebook (now Meta), to process Wi-Fi signal data. With this, they were able to create 2D digital representations of people present in the environment—similar to a virtual body map. Although the model is currently limited to 2D images, the team plans to expand its capabilities to generate 3D models in the future.
What’s most impressive is that all of this happens without invading privacy. Unlike cameras, which capture clear images of faces and details, the Wi-Fi-based system creates only abstract shapes, preserving individual identities.
Why Is This Important?
Beyond sounding like something out of an episode of Black Mirror , this technology has surprisingly practical applications:
1. Elderly Monitoring:
Imagine being able to ensure the safety of elderly individuals without intrusive cameras. The system can detect falls, suspicious movements, or even verify if a person is following their normal daily routine.
2. Home Security:
Forget conventional alarms. With this technology, it’s possible to detect unauthorized movements inside the house, even if the intruder is in a different room.
3. Smart Homes:
Smart homes can use this data to automatically adjust lighting, temperature, and other devices based on the presence and activities of occupants.
4. Health and Well-being:
In hospitals or clinics, the technology can remotely monitor patients, allowing for quick interventions in emergencies.
But What Are the Challenges?
Despite its promise, the technology still faces some obstacles before becoming widely accessible:
• Interference and Obstacles:
Wi-Fi signals can easily be blocked by thick walls or interfered with by other electronic devices, making the system less reliable in complex environments.
• Privacy and Regulation:
While considered “private,” collecting data on human movements raises ethical questions. Regulations like GDPR (in Europe) require transparency and explicit consent for any type of monitoring, even if it doesn’t involve images.
• Cost and Infrastructure:
Many Wi-Fi routers currently on the market aren’t designed to provide the detailed data needed for this type of analysis. Updating infrastructure could be expensive, especially for large commercial or public spaces.
The Future Is Coming
As 5G and, eventually, 6G networks become more widespread, the accuracy and speed of these systems are expected to increase exponentially. There are already plans to integrate neural processing units (NPUs) directly into routers, enabling them to process data locally and in real-time, reducing latency and improving privacy.
And while alternative technologies like mmWave radar and LiDAR offer other ways to detect humans, they are much more expensive and consume more energy. Using Wi-Fi, on the other hand, is scalable and leverages existing infrastructure in millions of homes and offices.
A New Era of Invisible Monitoring
This innovation demonstrates how everyday items, like Wi-Fi routers, can be transformed into powerful tools to solve real-world problems. At the same time, it reminds us of the importance of balancing convenience and privacy. After all, who would have imagined that the simple Wi-Fi connection in our homes could one day “see” beyond walls?
If you found this news story curious and bizarre, get ready: the future is about to get even stranger—and more fascinating.
Want to know more about groundbreaking technologies? Keep following our site to stay updated on the most bizarre and curious news from around the world!